Curriculum for the Master´s Programme in Computer Science (IT) 2017
1: Preface
Pursuant to Act 261 of March 18, 2015 on Universities (the University Act) with subsequent changes, the following curriculum is established. The programme also follows the Joint Programme Regulations and the Examination Policies and Procedures for The Faculty.
2: Basis in Ministerial orders
The Master’s programme is organised in accordance with the Ministry of Higher Education and Science’s Order no. 1328 of November 15, 2016 on Bachelor’s and Master’s Programmes at Universities (the Ministerial Order of the Study Programmes) and Ministerial Order no. 1062 of June 30, 2016 on University Examinations (the Examination Order). Further reference is made to Ministerial Order no. 111 of January 30, 2017 (the Admission Order) and Ministerial Order no. 114 of February 3, 2015 (the Grading Scale Order) with subsequent changes.
3: Campus
The programme is offered in Aalborg.
4: Faculty affiliation
The Master’s programme falls under The Technical Faculty of IT and Design, Aalborg University.
5: Study board affiliation
The Master’s programme falls under Study Board of Computer Science
6: Affiliation to corps of external examiners
The Master’s programme is associated with the external examiners corps on Computer Science
7: Admission requirements
Applicants with a legal right of admission (retskrav)
- Bachelor’s degree in Information Technology with Specialisation in Technology from Aalborg University
Applicants without legal right of admission
Students with Bachelor’s degree in Computer Science or Software Engineering may, upon application to the Board of Studies, be admitted after a specific academic assessment if the applicant is deemed to have comparable educational prerequisites. The University can stipulate requirements concerning conducting additional exams prior to the start of study.
All students applying must document English language qualifications comparable to an ‘English B level’ in the Danish upper secondary school (minimum average grade 02).
8: The programme title in Danish and English
The Master’s programme entitles the graduate to the Danish designation Cand.scient. i datalogi (it). The English designation is: Master of Science (MSc) in Computer Science (IT).
9: Programme specifications in ECTS credits
The Master’s programme is a 2-year, research-based, full-time study programme. The programme is set to 120 ECTS credits.
10: Rules concerning credit transfer (merit), including the possibility for choice of modules that are part of another programme at a university in Denmark or abroad
The Study Board can approve successfully completed (passed) programme elements from other Master’s programmes in lieu of programme elements in this programme (credit transfer). The Study Board can also approve successfully completed (passed) programme elements from another Danish programme or a programme outside of Denmark at the same level in lieu of programme elements within this curriculum. Decisions on credit transfer are made by the Study Board based on an academic assessment. See the Joint Programme Regulations for the rules on credit transfer.
11: Exemptions
In exceptional circumstances, the Study Board study can grant exemption from those parts of the curriculum that are not stipulated by law or ministerial order. Exemption regarding an examination applies to the immediate examination.
12: Rules for examinations
The rules for examinations are stated in the Examination Policies and Procedures published by the faculty on their website.
13: Rules concerning written work, including the Master’s Thesis
In the assessment of all written work, regardless of the language it is written in, weight is also given to the student's formulation and spelling ability, in addition to the academic content. Orthographic and grammatical correctness as well as stylistic proficiency are taken as a basis for the evaluation of language performance. Language performance must always be included as an independent dimension of the total evaluation. However, no examination can be assessed as ‘Pass’ on the basis of good language performance alone; similarly, an examination normally cannot be assessed as ‘Fail’ on the basis of poor language performance alone.
The Study Board can grant exemption from this in special cases (e.g., dyslexia or a native language other than Danish).
The Master’s Thesis must include an English summary (or another foreign language: French, Spanish or German upon approval by the Study Board). If the project is written in English, the summary must be in Danish (The Study Board can grant exemption from this). The summary must be at least 1 page and not more than 2 pages (this is not included in any fixed minimum and maximum number of pages per student). The summary is included in the evaluation of the project as a whole.
14: Requirements regarding the reading of texts in a foreign language
At programmes taught in Danish, it is assumed that the student can read academic texts in modern Danish, Norwegian, Swedish and English and use reference works, etc., in other European languages. At programmes taught in English, it is assumed that the student can read academic text and use reference works, etc., in English
15: Competence profile on the diploma
The following competence profile will appear on the diploma:
A Candidatus graduate has the following competency profile:
A Candidatus graduate has competencies that have been acquired via a course of study that has taken place in a research environment.
A Candidatus graduate is qualified for employment on the labour market based on his or her academic discipline as well as for further research (PhD programmes). A Candidatus graduate has, compared to a Bachelor, developed his or her academic knowledge and independence so as to be able to apply scientific theory and method on an independent basis within both an academic and a professional context.
16: Competence profile of the programme
The graduate of the Master’s programme
Knowledge
- has knowledge in computer science that, in selected areas, is based on the highest level of international research in the subject area
- can understand and, on a scientific basis, reflect over challenges in computer science and identify solutions to scientific and engineering problems
Skills
- are proficient in scientific methods and tools and general skills related to computer science
- can evaluate and select among the theories, methods, tools and general skills and, on a sound scientific and engineering basis, advance new analyses and solutions
- can communicate research-based knowledge and discuss professional, scientific and engineering problems with both peers and non-specialists
Competencies
- can manage work and development situations that are complex, unpredictable and require new solutions
- can independently initiate and implement discipline-specific and interdisciplinary cooperation and assume professional responsibility
- can independently take responsibility for own professional development and specialization
17: Structure and Contents of the programme
The programme is structured in modules and organized as a problem-based study. A module is a programme element or a group of programme elements, which aims to give students a set of professional skills within a fixed time frame specified in ECTS credits, and concluding with one or more examinations within specific exam periods. Examinations are defined in the curriculum.
The programme is based on a combination of academic, problem-oriented and interdisciplinary approaches and organized based on the following work and evaluation methods that combine skills and reflection:
- lectures
- classroom instruction
- project work
- workshops
- exercises (individually and in groups)
- teacher feedback
- reflection
- portfolio work
18: Overview of the programme
All modules are assessed through individual grading according to the 7-point scale or Pass/Fail. All modules are assessed by external examination (external grading) or internal examination (internal grading or by assessment by the supervisor only)
Offered as:
| |||||
| Module name | Course type | ECTS | Applied grading scale | Evaluation method | Assessment method |
1 Semester
| |||||
| From Reality to Models | Project | 15 | 7-point grading scale | Internal examination | Oral exam based on a project |
| Programming Paradigms | Course | 5 | 7-point grading scale | External examination | Written or oral exam |
| Electives 1. semester | |||||
2 Semester
| |||||
| From Models to Reality | Project | 15 | 7-point grading scale | External examination | Oral exam based on a project |
| Software Engineering | Course | 5 | 7-point grading scale | External examination | Written or oral exam |
| Electives 2. semester | |||||
3 Semester
| |||||
| Pre-Specialisation in Computer Science | Project | 20 | 7-point grading scale | External examination | Oral exam based on a project |
| Entrepreneurship | Course | 5 | Passed/Not Passed | Internal examination | Written or oral exam |
| Electives 3. semester | |||||
4 Semester
| |||||
| Master’s Thesis | Project | 30 | 7-point grading scale | External examination | Oral exam based on a project |
Electives 1. semester | |||||
| Module name | Course type | ECTS | Applied grading scale | Evaluation Method | Assessment method |
| Computability and Complexity | Course | 5 | 7-point grading scale | External examination | Written or oral exam |
| Advanced Topics in Databases | Course | 5 | 7-point grading scale | Internal examination | Written or oral exam |
| Machine Intelligence | Course | 5 | 7-point grading scale | Internal examination | Written or oral exam |
| Advanced Topics in Human-Computer Interaction | Course | 5 | 7-point grading scale | Internal examination | Written or oral exam |
| Data-intensive Systems | Course | 5 | 7-point grading scale | Internal examination | Written or oral exam |
| Advanced Topics in Distributed Systems | Course | 5 | 7-point grading scale | Internal examination | Written or oral exam |
| Real-Time Systems | Course | 5 | 7-point grading scale | Internal examination | Written or oral exam |
| Web Engineering | Course | 5 | 7-point grading scale | Internal examination | Written or oral exam |
| Web Intelligence | Course | 5 | 7-point grading scale | Internal examination | Written or oral exam |
Electives 2. semester | |||||
| Module name | Course type | ECTS | Applied grading scale | Evaluation Method | Assessment method |
| Advanced Algorithms | Course | 5 | 7-point grading scale | Internal examination | Written or oral exam |
| Mobile Software Technology | Course | 5 | 7-point grading scale | Internal examination | Written or oral exam |
| Advanced Programming | Course | 5 | 7-point grading scale | Internal examination | Written or oral exam |
| Software Innovation | Course | 5 | 7-point grading scale | Internal examination | Written or oral exam |
| Languages and Compilers | Course | 5 | 7-point grading scale | External examination | Written or oral exam |
| Principles of Operation Systems and Concurrency | Course | 5 | 7-point grading scale | External examination | Written or oral exam |
| Advanced Topics in Machine Intelligence | Course | 5 | 7-point grading scale | Internal examination | Written or oral exam |
| Test and Verification | Course | 5 | 7-point grading scale | Internal examination | Written or oral exam |
| Advanced Topics in Modeling and Verification | Course | 5 | 7-point grading scale | Internal examination | Written or oral exam |
Electives 3. semester | |||||
| Module name | Course type | ECTS | Applied grading scale | Evaluation Method | Assessment method |
| Specialisation Course in Database Technology | Course | 5 | 7-point grading scale | External examination | Oral exam |
| Specialisation Course in Distributed Systems | Course | 5 | 7-point grading scale | External examination | Oral exam |
| Specialisation Course in Human-Computer Interaction | Course | 5 | 7-point grading scale | External examination | Oral exam |
| Specialisation Course in Semantic and Verification | Course | 5 | 7-point grading scale | External examination | Oral exam |
| Specialisation Course in Machine Intelligence | Course | 5 | 7-point grading scale | External examination | Oral exam |
| Specialisation Course in Systems Development | Course | 5 | 7-point grading scale | External examination | Oral exam |
| Specialisation Course in Programming Technology | Course | 5 | 7-point grading scale | External examination | Oral exam |
Problem Based Learning:
A compulsory course in Problem Based Learning (PBL) is offered as an integrated part of the project module to students not acquainted with PBL at Aalborg University
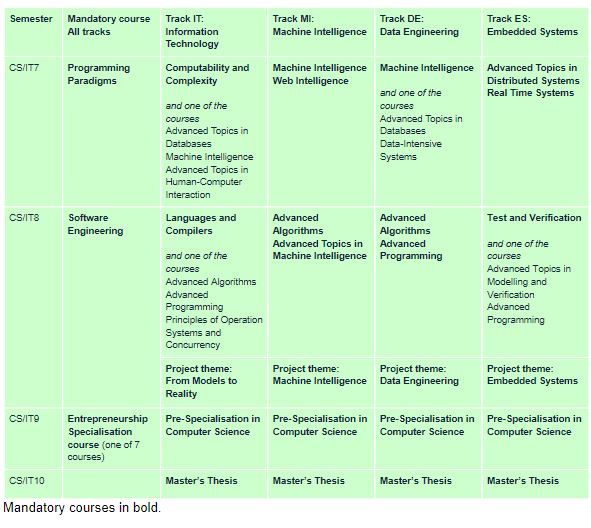
Tracks
After having been accepted to the programme, students are free to choose between the elective courses at IT7. Choosing one of the tracks below, i.e. Information Technology, Machine Intelligence, Data Engineering or Embedded Systems will give the student a coherent profile in the given track. Students are required to choose tracks at IT8. In addition to the tracks listed in the scheme below, it is also possible to create other combinations after a personal consultation with the Study Board. Students with a Bachelor's degree in Information Technology will be enrolled at the IT-track.
19: Additional information
The current version of the curriculum is published on the Board of Studies’ website, including more detailed information about the programme, including exams.
All students who have not participated in Aalborg University’s PBL introductory course during their Bachelor’s degree must attend the introductory course “Problem-based Learning and Project Management”. The introductory course must be approved before the student can participate in the project exam. For further information, please see the School of Information and Communication Technology’s website.
20: Commencement and transitional rules
The curriculum is approved by the Dean of The Technical Faculty of IT and Design and enters into force as of September 2017
21: Amendments to the curriculum and regulations
Minor editorial changes have been made in connection with the digitisation of the study curriculum